Project Revenue (Billing) is the total amount of money a Customer pays for a project. We will be getting Billable amount from customer.
Cost is the total funds needed to complete the project or work that consists of a Direct Cost and Indirect Cost. We will be getting cost from in house finance team.
The Operating Margin measures how much profit a company makes from the project on a dollar of sales after paying for variable costs of production, such as employee wages, software and hardware, but before paying interest or tax.
Case study:
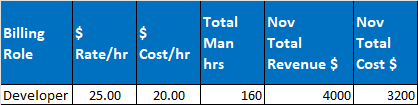
One developer working on a project which is planned to complete in one month (ie: 8 hrs/day * 20 days/month = 160 hrs).
Billable amount from the customer is 25$/hr and Cost from Employer is 20$/hr.
Revenue = $4000
Cost = $3200
Revenue Margin = Revenue - Cost = $4000-$3200 = $800
Revenue Margin Percentage (%) = (Margin/Revenue) * 100 = (800/4000)*100 = 20%
We can say that, the project is running with 20% profit.
Assume due to incorrect project requirement analysis and design we have signed contract for one developer but to complete the project we need one more developer with 50% utilization.
Now we will calculate the profit of the above.
After added 80 hrs of additional effort
Revenue = $4000 (Remains same)
Cost = $4800 (increased from $3200 to $4800)
Revenue Margin = Revenue - Cost = $4000-$4800 = -$800
Revenue Margin Percentage (%) = (Margin/Revenue) * 100 = (-800/4000)*100 = - 20%
We can say that, the project is running with 20% loss.


Comments
Post a Comment