Java and Project Manager are like bread and jam. We can’t separate both.
Java Technical project manager helps the team in design, troubleshooting and deployment the code.
We need to develop our skills on below:
OOP stands for Object-Oriented Programming.
Classes and objects are the two main aspects of object-oriented programming.
Core Java:
Core Java starts with Class/Objects, Class Attributes, Class Methods, Constructors, Modifiers (public, private, default, protected), Encapsulation(getter/setter), package, Inheritance (Subclass and Superclass), Polymorphism, Interface, Exceptions and much more.
Multithreading in Java is a process of executing two or more threads simultaneously to maximum utilization of CPU. Multithreaded applications execute two or more
threads run concurrently. Hence, it is also known as Concurrency in Java.
Each thread runs parallel to each other.
Multiple threads don’t allocate separate memory area, hence they save memory. Also, context switching between threads takes less time.
Benefits of Multithreading: Improved throughput. Simultaneous and fully symmetric use of multiple processors for computation
and I/O. Superior application responsiveness Improved server responsiveness Minimized system resource usage Program structure simplification Better communication
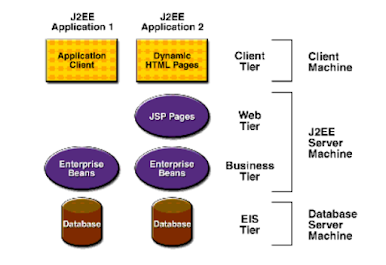
J2EE:
The J2EE application model is a multi-tier application model. Application components are managed in
the middle tier by containers. A container is a standard runtime environment that provides services,
including life cycle management, deployment, and security services, to application components.
This container-based model separates business logic from system infrastructure.
Design Pattern:
When we are developing software, some common problems like repetitive code, adding extra properties or redundant functions are bound to occur. Design patterns are smart and reusable solutions for these problems, saving considerable time and effort for developers.
Spring Core:
Core (spring-core) is the core of the framework that power features such as Inversion of Control and dependency injection. Beans (spring-beans) provides Beanfactory, which is a sophisticated implementation of the factory pattern.
Spring MVC:
A Spring MVC is a Java framework which is used to build web applications.
It follows the Model-View-Controller design pattern. It implements all the basic
features of a core spring framework like Inversion of Control, Dependency Injection.
A Spring MVC provides an elegant solution to use MVC in spring framework by the
help of DispatcherServlet. Here, DispatcherServlet is a class that receives the
incoming request and maps it to the right resource such as controllers, models,
and views.
Advantages of Spring:
- It is a lightweight framework.
- It does not support tag library.
- It has loosely coupled modules.
- It is integrated with ORM Technologies using which, lesser coding is required after and before the main logic.
- It has a layered MVC architecture containing 3 layers for modelling, viewing and controller.
Spring Batch:
A lightweight, comprehensive batch framework designed to enable the development of robust batch applications vital for the daily operations of enterprise systems. Spring Batch provides reusable functions that are essential in processing large volumes of records, including logging/tracing, transaction management, job processing statistics, job restart, skip, and resource management. It also provides more advanced technical services and features that will enable extremely high-volume and high performance batch jobs through optimization and partitioning techniques. Simple as well as complex, high-volume batch jobs can leverage the framework in a highly scalable manner to process significant volumes of information.
Web services SOAP/REST:
Database:








Comments
Post a Comment