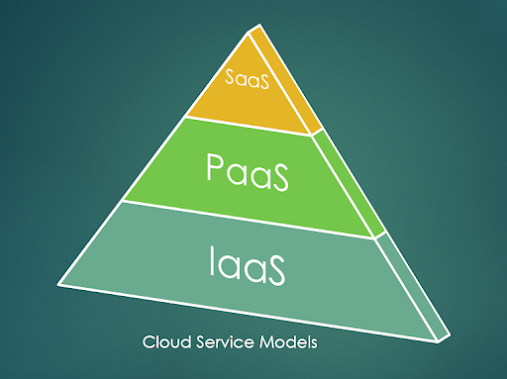
Cloud Service Models (IaaS,PaaS,SaaS):
IaaS:
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a type of cloud computing service that offers
- essential compute (hardware)
- storage
- networking resources on demand
- middleware (ex: Linux)
- OS
IaaS provides services on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Example for IaaS is EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) service provided by AWS.
AWS EC2 provides, processers, storages, networking, operating system.
PaaS:
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud, with resources that enable you to deliver everything from simple cloud-based apps to sophisticated, cloud-enabled enterprise applications.
Example for PaaS is AWS Elastic Beanstalk provided by AWS, for deploying applications which orchestrates various AWS services, including EC2.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is an easy-to-use service for deploying and scaling web applications and services developed with Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker on familiar servers such as Apache, Nginx, Passenger, and IIS.
SaaS:
Software as a service (SaaS) allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps over the Internet.
SaaS is also known as "On-Demand Software".
Common examples are email, calendaring and office tools (such as Microsoft Office 365), ERP, CRM, Sales, .
SaaS provides a complete software solution which you purchase on a pay-as-you-go basis from a cloud service provider.
Comments
Post a Comment